Numeric Method # The syntax of the chmod command when using numeric method has the following formatZIP command in Linux with examples;लिनक्स की कमांड (Linux Commands)bc Command Chmod command s dca notes in hindi Linux commands in hindi pgdca notes in hindi pgdca operating system notes in hindi 1 Comment Click here to post a comment Ritu gupta says March 12, 17 at 528 am

8 Pwd Command In Linux Top Commands In Linux Linux Commands For Beginners Hindi Youtube
Chmod command in linux in hindi
Chmod command in linux in hindi-Linux File Permission chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized personThe chmod command The chmod command lets you change the permissions for a Linux file Before explaining the syntax of the chmod command, you need to look at the cryptic way Linux reports file permissions Linux grants three different types of permissions — read, write, and execute — for three different scopes owner, group, and everyone



コレクション Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi
Linux commands chmod A quick guide to the `chmod` command, used to change the file mode Published Sep 23, Every file in the Linux / macOS Operating Systems (and UNIX systems in general) has 3 permissions Read, write, execute Go into a folder, and run the ls al commandAdd the file's owner permissions to the permissions that the members of the file's group have chmod gu filename;This tutorial explains CHMOD and CHOWN commands that are broadly used in Linux CHMOD and CHOWN The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or DirectoryThe Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners
Replace directory with the directory path that holds the files and subdirectories you want to configure Specify whether it is searching for a directory type d or a file type f Set the file privilege with the chmod command using the numerical or symbolic modeChmod stands for " Change Mode " and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups ( Owner, Group and Other) in Linux The command is relatively simple to use and involves using chmod, followed by the permissions you want to set, then the name of the directory or file you want to modifySudo find directory type d/f exec chmod privilege {} \;
In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file It is used to change the permission for files and folders These permissions are given to file/folder to provide a secure environment to the OS, efficient management of a file and highlevel access to the users accessing the files/ folders3 chmod examples Syntax and Options Related Commands What is chmod?Head command in Linux with examples Difficulty Level Easy;


Why I Switched To Ubuntu Linux And Then Returned To Windows By Ishaan Kalorano Khaperde Nov Medium



Complete List Of Useful Ubuntu Linux Commands For Programmers
Last Updated August 28th, 19 by Hitesh J in Guides The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linuxbased operating systems The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain modeThe chmod command stands for change mode and it's used to limit access to resources It's a same as using your mouse to rightclick a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs and defining who can access the resource the chmod command is the way to do it on the command lineUsing chmod Command Chmod कमांड का सामान्य रूप निम्नलिखित रूप लेता है $ chmod OPTIONS MODE FILE Use Symbolic method in chmod Command


Blackfear Host Blackfearh Profile Pinterest



Pongoos
Add a sticky bit to a given directory chmod ot dirname;If you are new to Linux, and are looking for a way to change file/directory permissions through the command line, you'll be glad to know there exists a command dubbed chmod that lets you easily do this In this tutorial, we will discuss the basics of this command as well as provide examples explaining how it can be used in various scenariosWhatsApp Facebook Twitter Email



Hindi Linux File Ownership And Permissions Youtube



Linux Command In Hindi Part 8 Youtube
As you may know, the chmod (stands for Ch ange mod e) command is used to set or change the access permissions of a file or directory in Unixlike systems So if the executable permission of chmod is removed, you can't assign the permissions to any programs, including the chmod command itselfS chmod command chmod command in linux chmod command in linux in hindi linux chmod command Linux file permission Use Numeric Method in chmod command Use Symbolic method in chmod Command लिनक्स में chmod कमांड क्या हैं?The chmod command name stands for "change mode", and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files I'll start with some simple examples, then add some more details as we go along



最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた


1
In this method, you can run the "ld" loader directly, and pass it the command you want to run like below # /lib64/ldlinuxx8664so2 /usr/bin/chmod x /usr/bin/chmod If you use 32 bit systems, the command would be $ /lib/ldlinuxso /usr/bin/chmod x /usr/bin/chmodLs command in linux in hindi ls कमांड के उपयोग से किसी भी डायरेक्टरी में मौजूद सभी फ़ाइल के नाम को प्रदर्शित किया जा सकता है अर्थात इससे पता चलता है कि यूजर वर्तमान समय पर जिस डायरेक्टरी में है उसमें कौनकौन से फाइल मौजूद है।How to use the chmod command in Linux First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux Chmod {user}{add or remove permission}{permoission}



Swift 4 Xcode 9 How To Use Auto Layout Constraints And Size Classes Objective C Ios App Development Ios



Verify Technology Posts Facebook
Last Updated August 28th, 19 by Hitesh J in Guides The chmod and chown commands are powerful and most popular command line tool that can be used to control access to files in Linuxbased operating systems The chmod also called change mode that is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain modeCauses them to be removed;This video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change modeBoth Octal and symbolic modes


2



Solaris Pocket Survival Guide Booting Command Line Interface
Last Updated 21 May, 19;TCP ServerClient implementation in C;The difference is what permissions get set and which mode you use to set them With chmod x you set the executable bit for all the owner, the owner group, and the other users This is known as symbolic mode To quote the man chmod The operator causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file;



Linux Cli Advance Commands File Directory Permissions Chmod Hindi Urdu Part 9 Youtube



How To Install Virtual Box Guest Addition On Kali Linux Simple Method Summary Networks
Chmod ux scriptsh As you'd have guessed, 'ux' says grant () the owner/current user (u) execute (x) access to the file Similarly, for group, you can use 'g' and for others you can use 'o' Please note that whenever you want to grant/revoke a common set of permissions to/from all, you can use 'a' instead of 'ugo'Chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r myfile This example uses symbolic permissions notation The letters u, g, and o stand for " user ", " group ", and " other " The equals sign (" = ") means "set the permissions exactly like this," and the letters " r ", " w ", and " x " stand for "read", "write", and "execute", respectivelyThe chmod command modifies the permission mode of objects in the system It is one of the most used and important commands in the set of Linux security commands A plus () symbol adds a permission, and a minus () symbol removes a permission You can read chmod ur as "user plus read," as it gives the user read permission
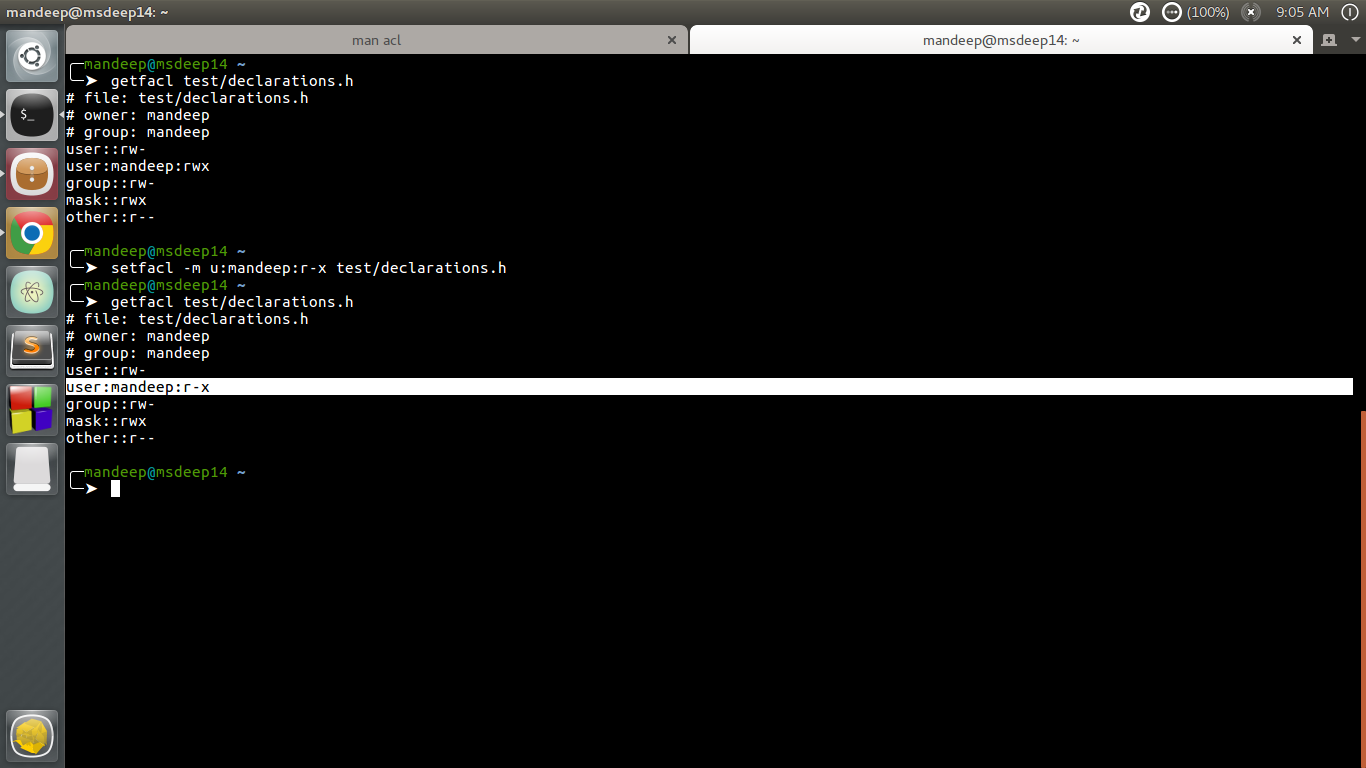


Access Control Lists Acl In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Calameo Intro Linux
Linux users are searching for a way via the command prompt to modify the file/directory permissions Chmod modifies each document's rights by mode, in which the mode specifies the privileges to be updated You may designate a mode with octal numerical or letters In this article, Linux Chmod Command Tutorial for Beginners is explainedIn this tutorial, I am going through the steps to create a bash script and to make the script executable using the chmod command After that, you will be able to run it without using the sh or bash commands Step 1 Creating a Bash File The first step is to create a new text file with sh extension using the following command $ touch helloMy Website http//aapkabazarinUnix Shell Scripts https//googl/zedFG9Unix Shell Commands Beginner TutorialsFile Permission Directories Permission;



How To Use Chmod 777 Command In Linux Explained How To Use Chmod Command Hindi Tutorial Youtube



Linker Computing Wikipedia
About chmod command The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE The chmod command stands for change mode and it's used to limit access to resources It's a same as using your mouse to rightclick a file or folder and selecting the permission tabs andChmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command outputChmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file



Innovatiive Education 帖子 Facebook


Q Tbn And9gctzdlykpjcvke B Rtcizslek0layqek R6mtith2lew3v1r Fp Usqp Cau
TCP ServerClient implementation in C;Introduction to chmod Command in Linux In Linux/Unix like operating system, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file It is used to change the permission for files and folders These permissions are given to file/folder to provide a secure environment to the OS, efficient management of a file and highlevel access to the users accessing the files/ foldersChmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file


2



Ubuntu 16 04 Server With Lemp Par Wordpress Install Kaise Kare
Last Updated 21 May, 19;By Magesh Maruthamuthu · Last Updated August 22, 19 As Linux administrator, we always use chmod command to change file permissions in Linux It may happens many times in a day, it depends on your environment size and team size It could be a single file or multiple files If it's in the same directory, you may need to use chmod command with file name and new file permission to be appliedThis Linux chmod command tutorial shows you to change file permissions including mode, octal and binary of files and directories with examples and syntax FactorPad Linux Essentials playlist



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



Linuxtutorial
By Magesh Maruthamuthu · Last Updated August 22, 19 As Linux administrator, we always use chmod command to change file permissions in Linux It may happens many times in a day, it depends on your environment size and team size It could be a single file or multiple files If it's in the same directory, you may need to use chmod command with file name and new file permission to be appliedIt is the complementary of Tail command The head command, as the name implies, print the top N number of data of the given input By default, it prints the first 10 lines of theThe chmod command lets you changes the access permissions of files and folders You may see a chmod command like this chmod 700 path/to/a/file What does the 700 mean?



How To Install Kali Linux On Android Without Root Full Version



How To Install Windows Powershell On Kali Linux Pentestblog
$ chmod gx appsh Change File Mode For Other Others is special group which covers all users in a Linux system We can enable the execution right of the all users in a file with o like below $ chmod ox appsh Change File Mode For All In some cases we can see the x without a definitionChmod Command in Linux (File Permissions) Chmod_Command_in_Linuxpng In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command to change the access permissions ofZIP command in Linux with examples;



Computer Linux Command All Comptetive Exams In Hindi By Study Hub



Installing Kali Nethunter On Unrooted Android Device Full Tutorial In Hindi
लिनक्स में chmod कमांड (Chmod Command in Linux) What is chmod Command?Head command in Linux with examples Difficulty Level Easy;The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images



09 Unix Linux Shell Soft Hard Links Ln Command By Mohammedi Computers
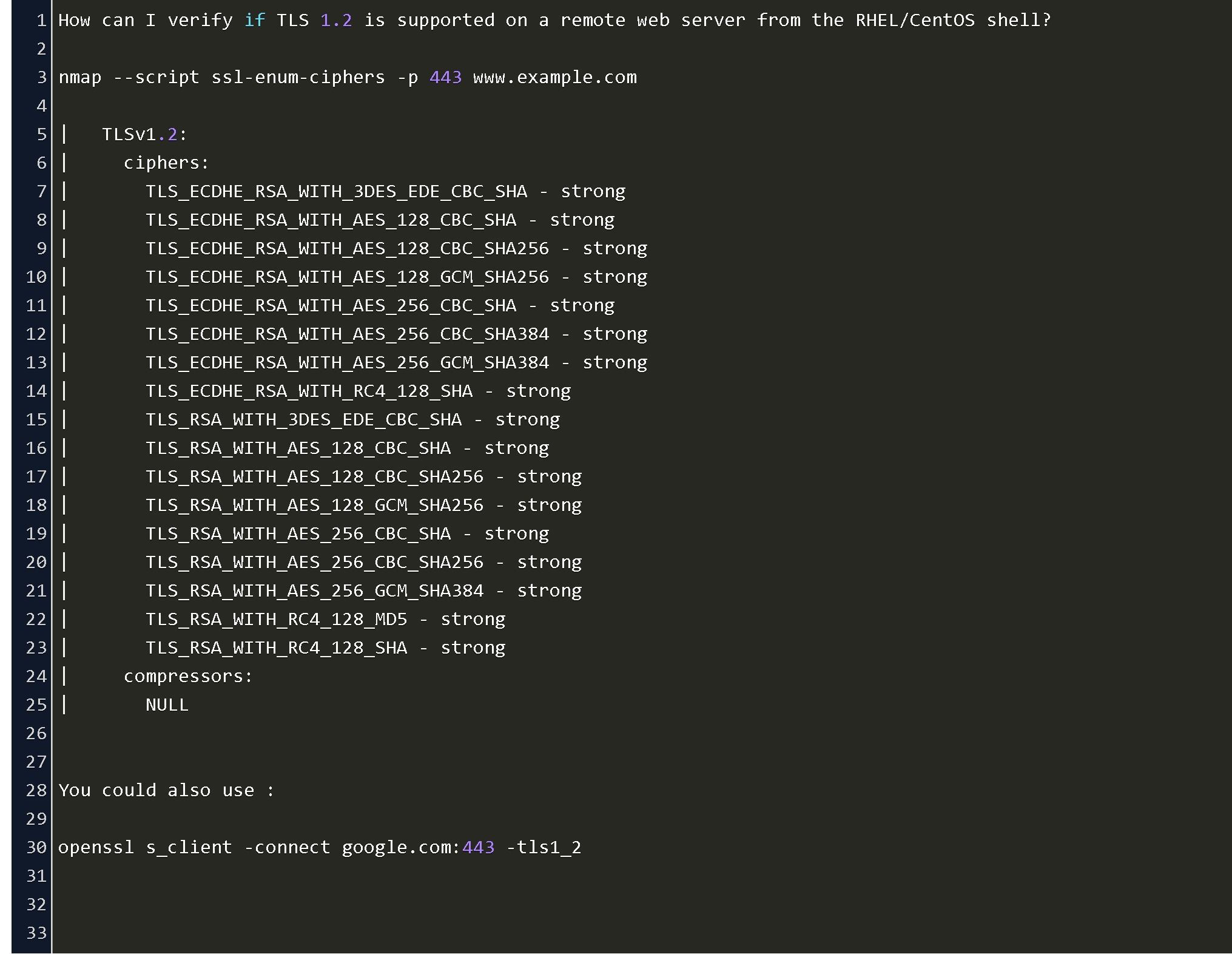


Openssl Command To Check Tls Version Code Example
Linux Operating Systyem Commands in Hindi Example of Popular Linux Command in Hindi Example of Popular Linux Command in Hindi लिनक्स ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम में 2700 से 3000 तक कमांड है, इन कमांड को जांचने के लिए भी एक कमांड है अर्थात अगर कोईChmod Unix, Linux Command chmod To change access permissions, change mode chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters OPTIONSChmod Unix, Linux Command chmod To change access permissions, change mode chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters OPTIONS
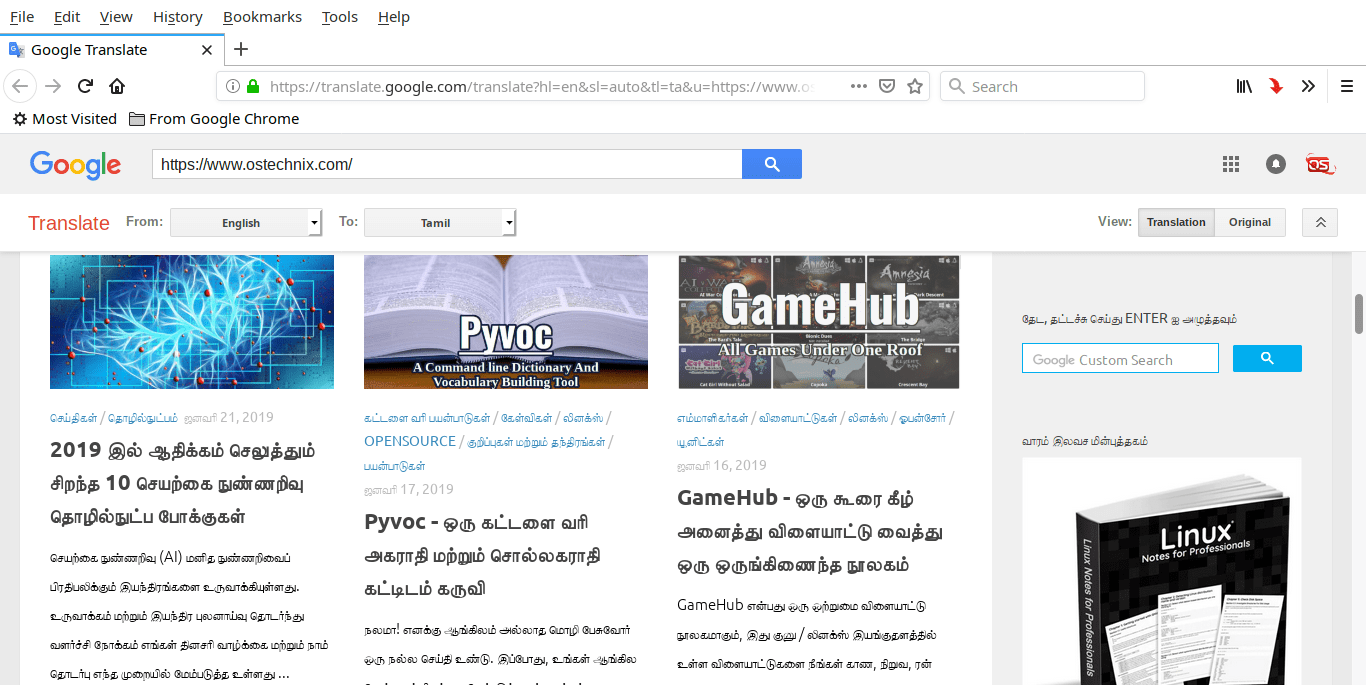


How To Use Google Translate From Commandline In Linux Ostechnix



コレクション Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi
Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2It is the complementary of Tail command The head command, as the name implies, print the top N number of data of the given input By default, it prints the first 10 lines of theChmod u=rw,g=rw,o=r documentdocx It's also possible to add permissions incrementally For example, we can add write permissions for others chmod ow documentdocx Or similarly, we can take away write access for the group by calling chmod gw documentdocx



Iotview Raspbian Sudo Command Line Interface


2
(chmod कमांड क्या हैं?) आपके लिनक्स सिस्टम की हर वस्तु में एक परमिशन मोड होता है जोNow, let us see how chmod command can be used to change the access mode of a file Example 1 Let's change the assgn1_clientc permission so that the owner cannot write(w) in the file but can only read it BEFORE rwrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc COMMAND chmod u=r assgn1_clientc AFTER rrwr mik mik assgn1_clientc BeforeAnd = causes them to be
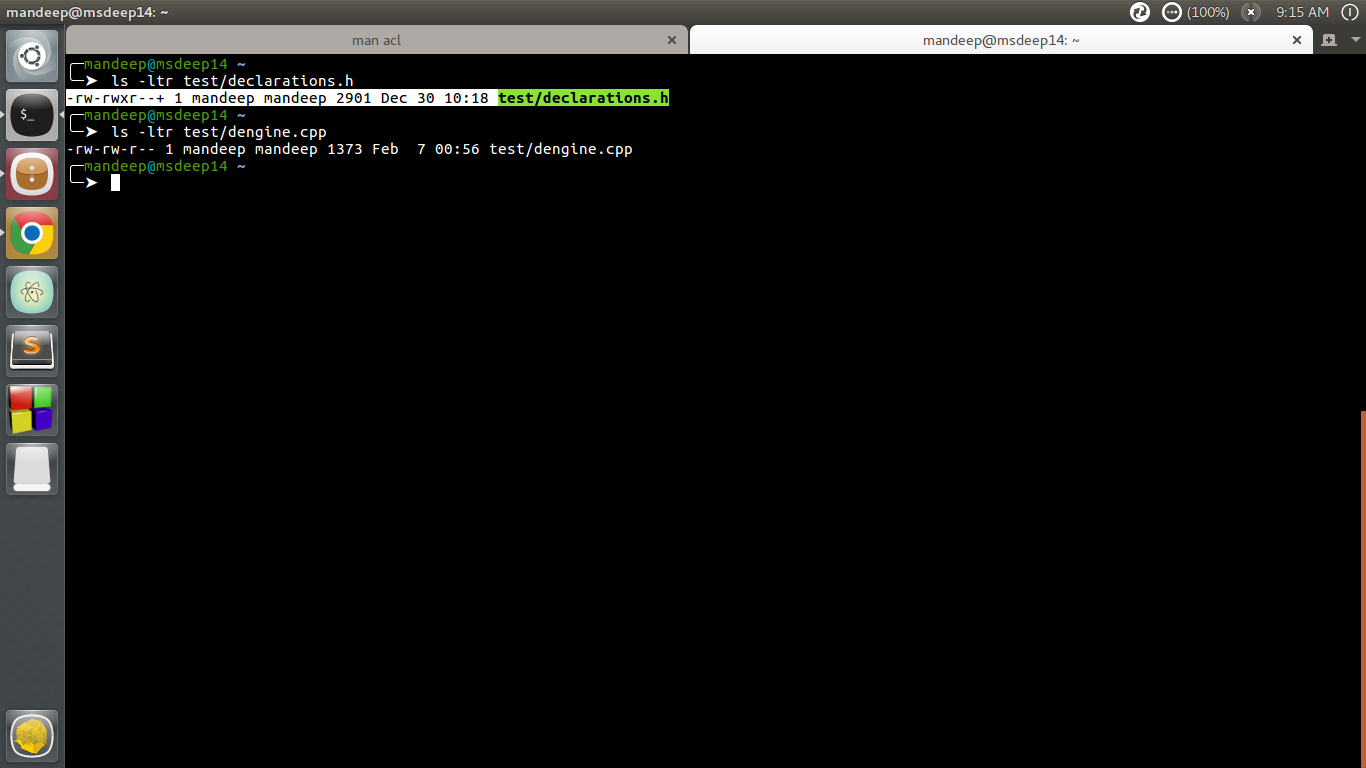


Access Control Lists Acl In Linux Geeksforgeeks



Use Scp Command In Linux To Copy Files Securely Over Ssh Protocol
This video explains chmod and chown commands part 1 https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=kzRZVjHatuo user management in linuxhttps//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=iI'll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod r Before you see the chmod examples, I would strongly advise you to learn the basics of file permissions in Linux Using chmod command will be a lot easier once you understand the permissionsChmod Recursive # The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, (recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows



How To Customize Rhel 8 0 Linux Terminal Urdu Hindi



Commands And Tools For Termux For Android Apk Download
Chmod stands for " Change Mode " and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups ( Owner, Group and Other) in Linux The command is relatively simple to use and involves using chmod, followed by the permissions you want to set, then the name of the directory or file you want to modifyIn this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user's file system Let's play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu Linux Permissions Linux Permissions are a great set of rules whichChmod commands in Hindi chmod शब्द का अर्थ "Change mode" है। यह कमांड फाइल या फोल्डर डायरेक्टरी को read, write और execute करने का एक्सेस अधिकार (Access Permission) बदलने के लिए उपयोग



Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi より興味深い壁紙fhd



Hindi Linux What Is Chmod And How To Use Chmod In Linux Youtube
What are file permissions and chmod command in Linux Chmod is an easy command in Linux However, it becomes difficult when you use all of its variations This command executes in so many ways Nevertheless, you need to know about file permissions File permissions decide whether a file is readable, writable, or bothChmod u=rw,og= ~/ssh/id_rsa or chmod 600 ~/ssh/id_rsa We should note that many Linux security configurations will prevent keys in the ssh folder from being used to allow SSH access if they do not have the correct permissions applied 64 Make a Script ExecutableUnix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2



Hindi Install Kali Linux 19 Without Termux Root Anlinux One Click By Nitish Kumhar



Linux For Ethical Hackers Kali Linux Tutorial Digital Ocean Promo Code
The chmod command allows a user to grant or revoke the read, write, and execute using various methods like numeric mode, symbolic, or reference file Syntax To change permission is the only right of the root user and owner of the file to change the permission of root user fileSometimes we need to change the ownership and group permission for any file or folder from the terminal This task can be done easily by using the `chown` command The uses of `chown` command are shown in this tutorial by using different examples



Building An Android Command Line Application Using The Ndk Build Tools Digit
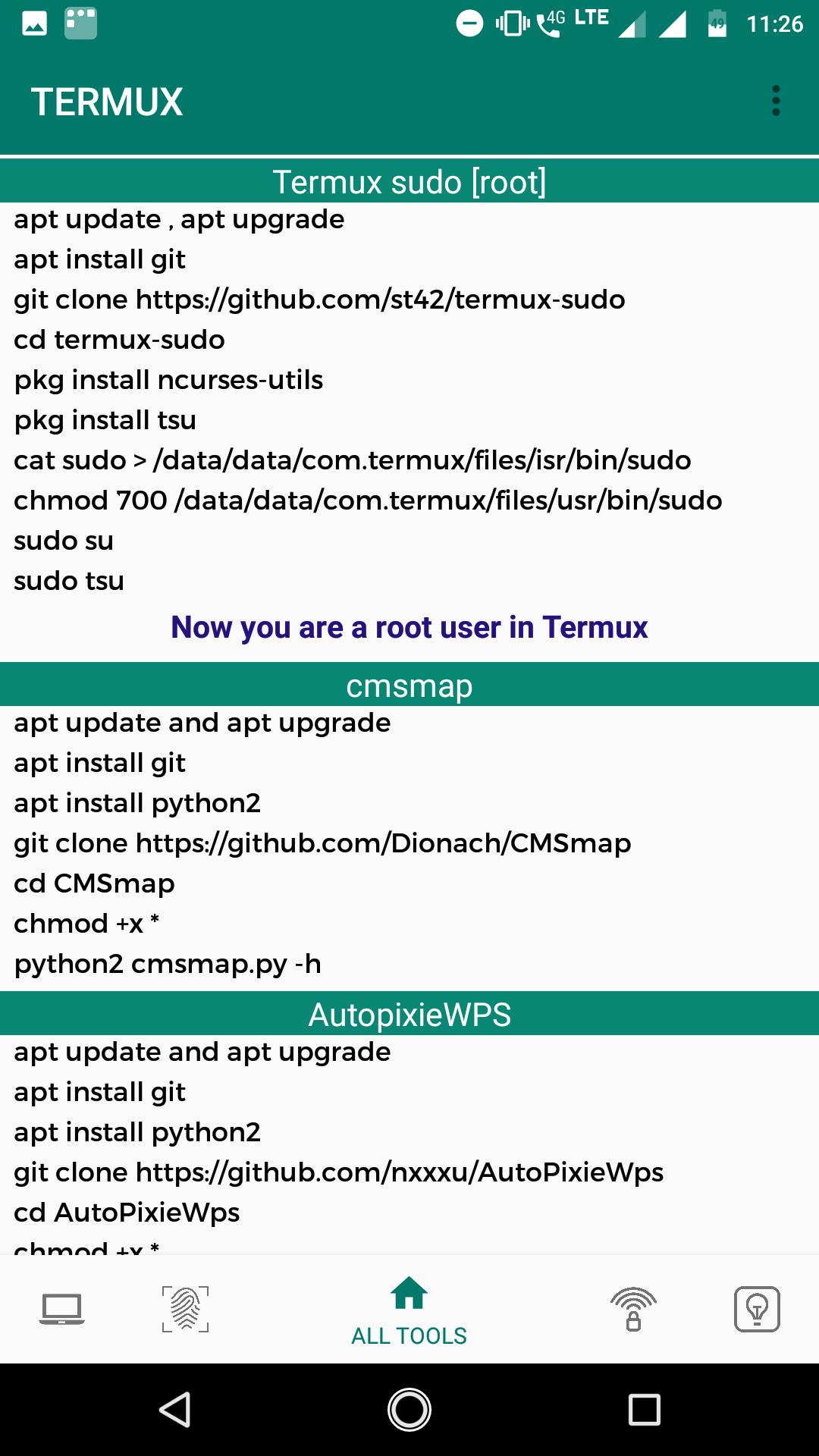


Commands And Tools For Termux For Android Apk Download



How To Remove Directory In Linux By Command And Gui Guide For Beginners



5 Best ह क ग कम ड क ज नक र Hacking Commands In Hindi



Configure Postfix Send With Gmail Smtp Relay Hindi Benisnous



Innovatiive Education Posts Facebook



Cobra Hacker 786 How Hack Using Termux



Linux Nice Re Nice Commands Process Hindi By Ethical Harsh



Verify Technology Posts Facebook



08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube



Linuxtutorial



Linux In Hindi Rhel 7 Selinux Part 3 Seven Layer Technologies Lucknow By Ravinder Singh Sahota



Linux Help Topics



Computer Linux Command All Comptetive Exams In Hindi By Study Hub



How To Use Say Cheese In Termux Say Cheese Termux Tutorial



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



コレクション Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi
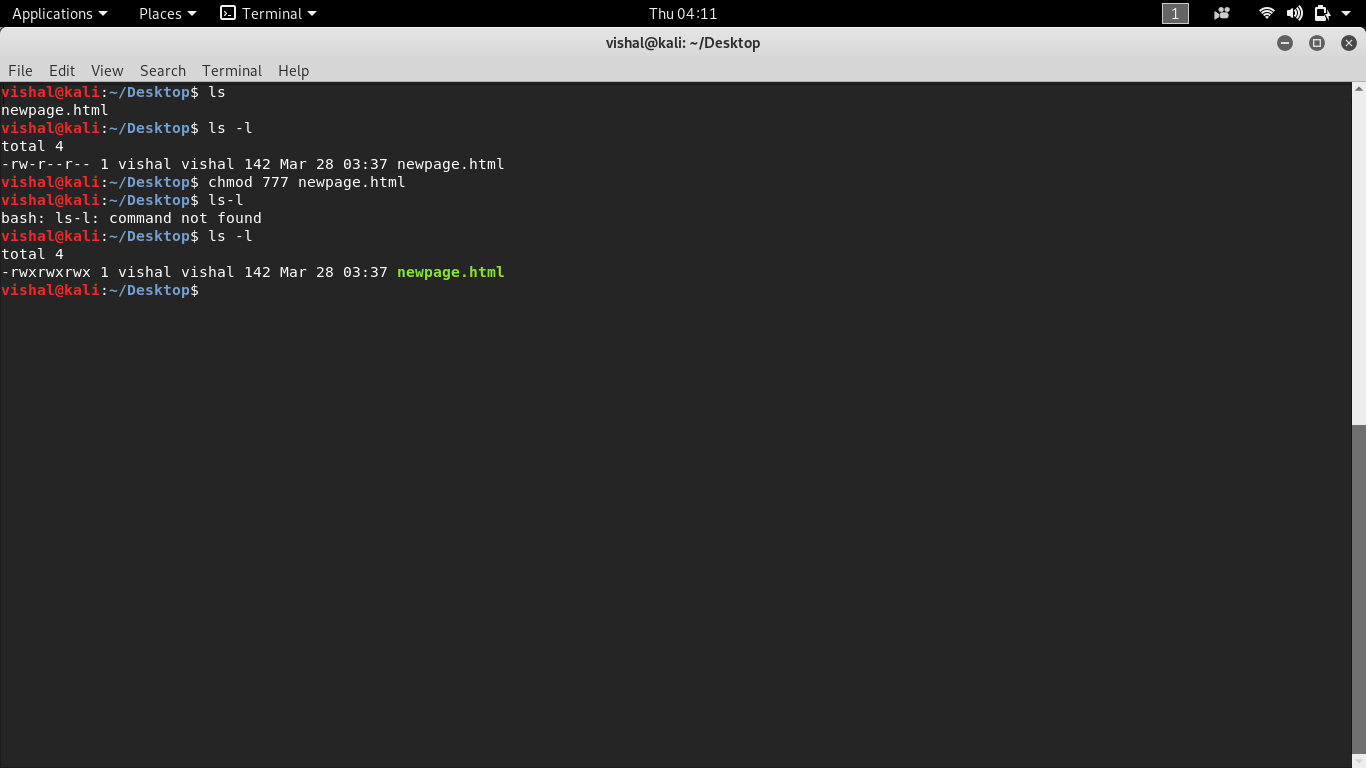


Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example



How To Install The Native Gams Version On Linux Digital Ocean Promo Code



Ubuntu Change Su Password Code Example



Learn Red Hat Linux Episode 14 File Folder Ownership And Permissions Commands Chown Chmod Benisnous



Linux Command Line Interface Chmod Command In Hindi Youtube



Touch Command In Unix By A Onetutors



Nethunter Rootless Kali Linux Documentation



How To Use Google Translate From Commandline In Linux Ostechnix



Pin On aaa



About Kaali Linux 17
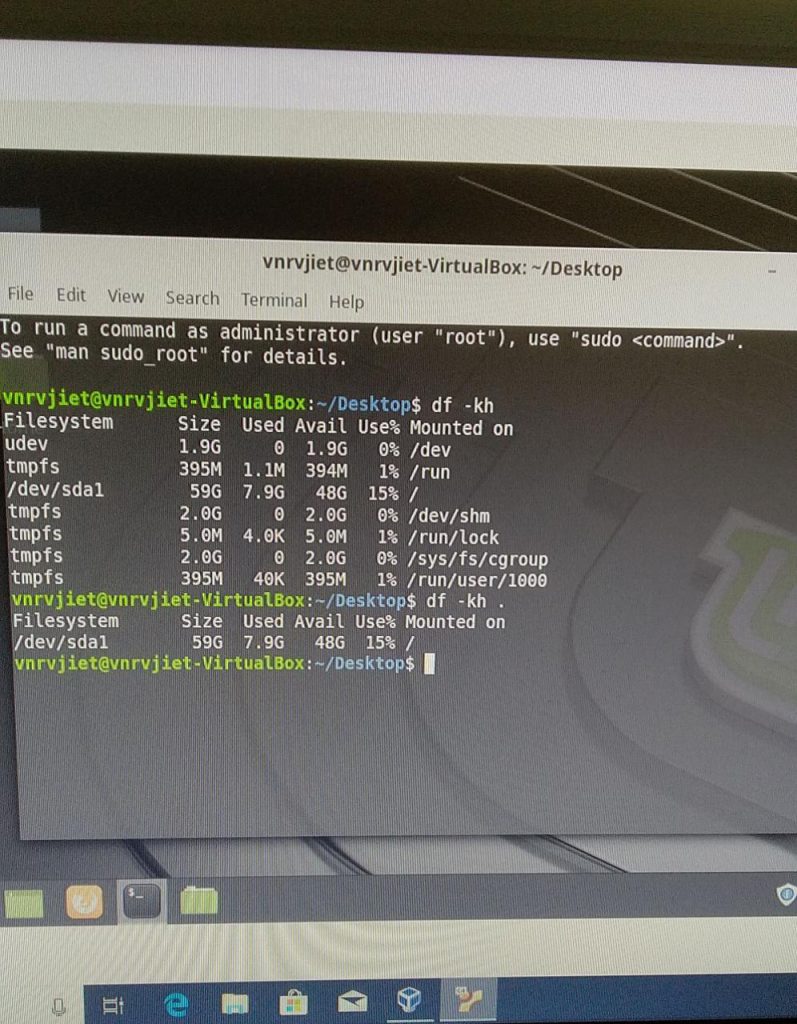


Probable Errors While Installing Vsdflow And Its Solutions Vlsi System Design
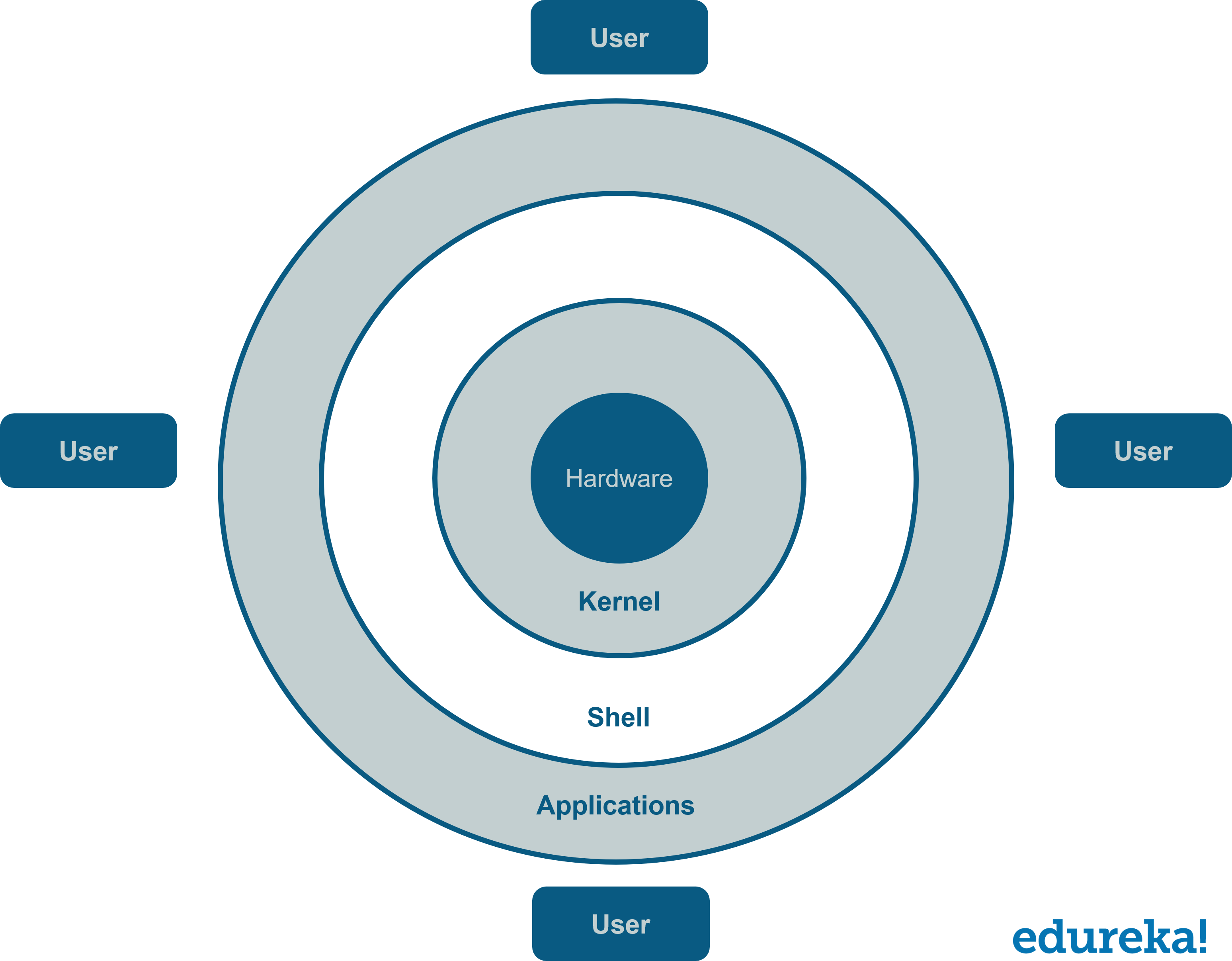


Linux Tutorial Linux Command Line Tutorial Linux Installation Edureka


Building An Android Command Line Application Using The Ndk Build Tools Digit



Chmod Date More Pr Linux Command Practical In Hindi Youtube



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



Probable Errors While Installing Vsdflow And Its Solutions Vlsi System Design



30 Basics Linux Command In Hindi



Move Between Directories Complete Linux Course Class 3 Urdu Hindi 21 Benisnous



Howto Installation Of Centos 6 X Server With Asterisk 11 And Freepbx 12 Voipsupport


How To Install Debian Testing Release Linux Hint



Ubuntu Karmic Booting Computer Architecture



Oracle Apps Dba Oracle R12 1 2 Install Guide On Linux 6 3 64bit



Pazeidimas Diskriminacinis Riaumoti Ubuntu Wc Yenanchen Com



Security


Getting Hardware Information From Linux To Help Forum Staff Page 2 Linux Org


Ratatosk



Verify Technology Posts Facebook



09 Unix Linux Shell Soft Hard Links Ln Command By Mohammedi Computers



Setting Up Emby Server On Linux Zap



Verify Technology Posts Facebook



Kill Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Kali Linux Tutorial 18 Archives Skynet Tools



How To Build Your Own File Server Computer Knowledge Hacking Computer Computer Projects



8 Pwd Command In Linux Top Commands In Linux Linux Commands For Beginners Hindi Youtube



कर नल क य ह Computer Hindi Notes



How To Install Windows Powershell On Kali Linux Pentestblog



Linux Command Line Tutorial Shell Basics


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた



Linux In Hindi Rhel 7 Selinux Part 3 Seven Layer Technologies Lucknow By Ravinder Singh Sahota



Change Themes In Termux In Cool Technology Channel Youtube


最も好ましい Chmod Command In Linux In Hindi さもがた


